Every website begins with a domain name. It acts as the address that connects users to your site. Understanding how domain names work helps you navigate the web and manage your online presence effectively.
This article explains the process step by step.
What Is a Domain Name?
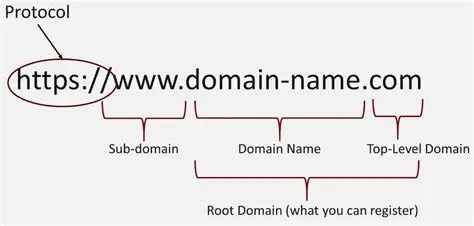
A domain name is a human-friendly address for a website. Instead of typing long numerical IP addresses, users type something simple like example.com. The domain name directs the browser to the correct server where the website is stored.
In short, a domain name bridges the gap between humans and machines on the internet.
The Role of DNS
When you enter a domain name in your browser, the Domain Name System (DNS) takes over. DNS acts like an online phonebook. Its job is to translate the domain name into an IP address that computers can understand.
For example, example.com might correspond to an IP like 192.0.2.1. DNS ensures this translation happens almost instantly, allowing browsers to find the correct server quickly.
How Browsers Find Websites
Once the DNS provides the IP address, your browser contacts the web server at that location. This server stores all the website’s files, such as text, images, videos, and code.
The server then sends these files back to the browser. In just seconds, the website appears on the user’s screen. This seamless process makes browsing fast and reliable.
Secure Connections
Many websites use HTTPS to secure the connection. When you visit an HTTPS site, the browser checks for a security certificate. This certificate ensures that data shared between the user and server is encrypted and safe from interception.
Secure connections are essential for online shopping, banking, and sharing personal information.
Main Components of a Domain Name
A domain name has two primary parts. The first is the second-level domain. This is the main part you choose, like “google” or “amazon.” It often represents a brand or business.
The second part is the top-level domain (TLD), which appears at the end. Examples include .com, .org, and .net. Together, these parts form a complete, functional domain name.
Why Domain Names Matter
Domain names make the internet easier to use. They provide a memorable way for users to visit websites. A good domain also enhances trust and professionalism.
Additionally, domain names indirectly support SEO. Search engines consider domain relevance and clarity when ranking websites. A well-chosen domain can make your website more visible and credible.
Tips for Managing Domains
Choosing and managing a domain requires attention. Keep it short, simple, and easy to remember. Avoid numbers or hyphens, as they may confuse users.
Always register your domain through a reputable registrar. Renew it on time to avoid losing it. Consider enabling auto-renewal for peace of mind.
Final Thoughts
Domain names are the foundation of online navigation. They translate human-friendly addresses into machine-readable IPs. DNS, servers, and secure connections make this process seamless.
By understanding how domain names work, you can choose better addresses for your website. This knowledge ensures a smooth experience for both you and your visitors.